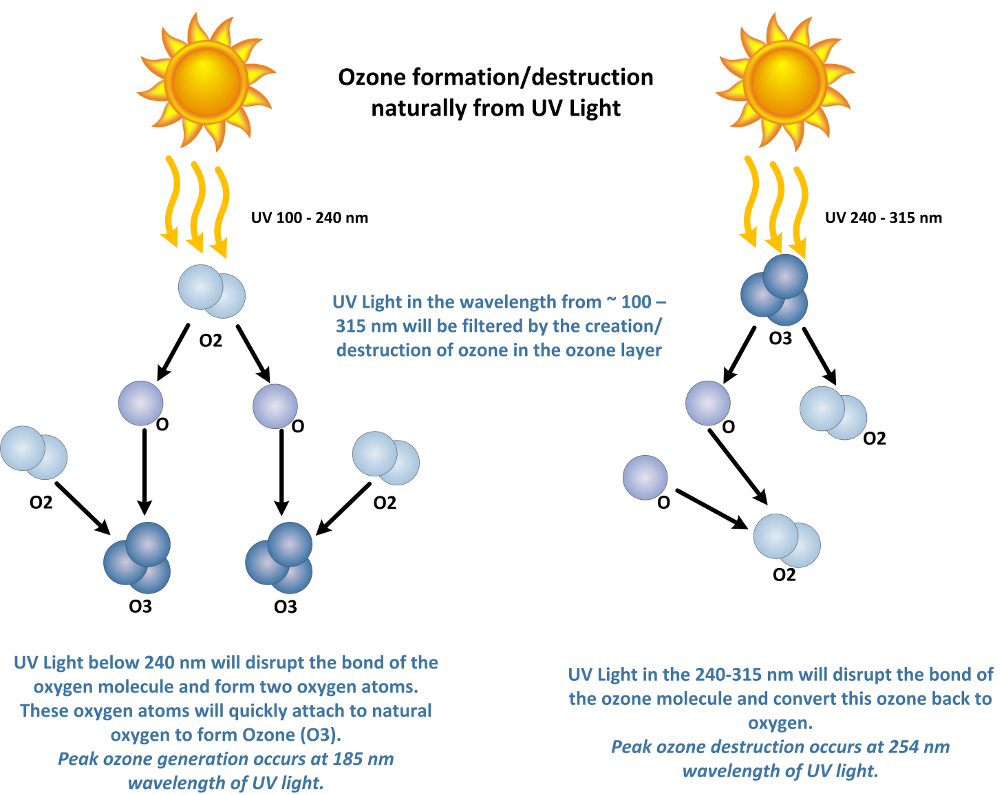
UV light will create ozone from atmospheric oxygen at short wavelengths of less than 240 nanometers (nm). UV light will also destroy ozone and break ozone back down into atomic oxygen (O) and diatomic oxygen (O2) at wavelengths from about 200 nm to 315 nm. Therefore, the ozone layer does a great job filtering UV wavelengths from about 100 – 315 nm. This is important as these are the harmful wavelengths of UV light that cause sunburn, and DNA damage in living tissues.
The ozone layer is an important part of our world’s stratosphere. The level of ozone in the stratosphere ranges from 2 to 8 ppm in the ozone layer, therefore most of the atmospheric oxygen remains in the diatomic form (O2).
Commercial Ozone Production from UV Light
The heart of every Ozone System is the Ozone Generator. Ozone (O3) is created from Oxygen (O2) in nature and also in Ozone Generators for commercial or industrial applications. However, Ozone (O3) quickly reverts back to molecular Oxygen (O2). Ozone cannot be stored due to a short half-life and must be produced on-site and on-demand. Therefore, the Ozone Generator is the most important component of any successful Ozone System.
Ozone can be produced commercially from an Ozone Generator using UV light. Ozone is produced from UV light wavelengths between 100 and 240 nm. A shortwave, low pressure UV lamp can be used for this purpose. These lamps will produce UV light with two peaks in the UV light band, one at 254 nm, and another at 185 nm. The 185 nm light is what is referred to as an “ozone producing” lamp, while the 254 nm light is referred to as a “germicidal” lamp.
Note: the 254 nm UV light is also used to break down ozone in air or water as UV light above 240 nm will photolyze ozone back to oxygen.