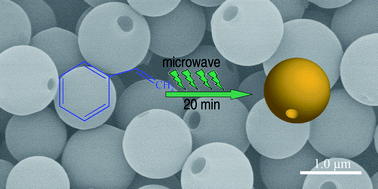
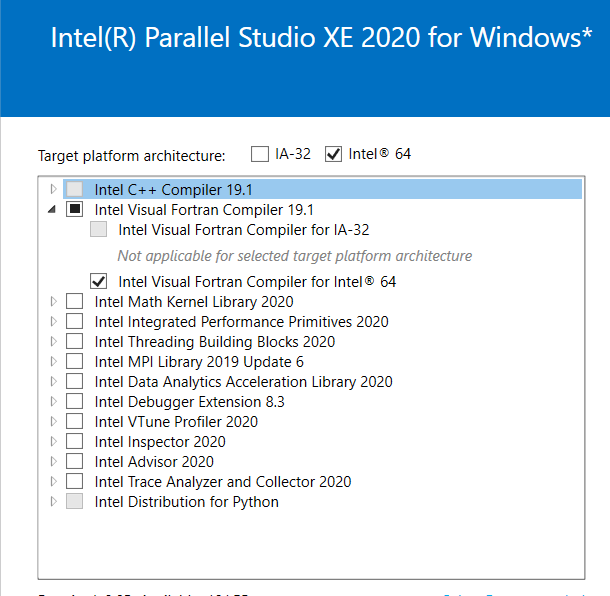
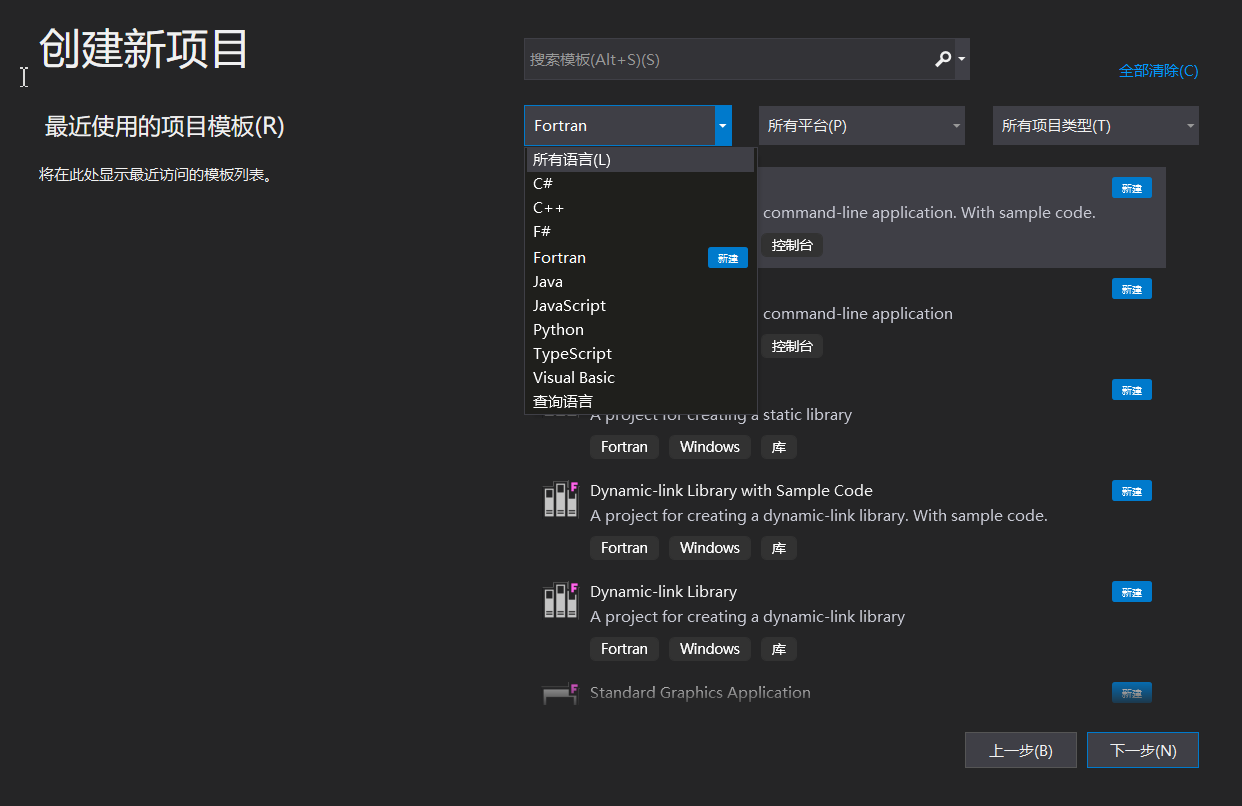
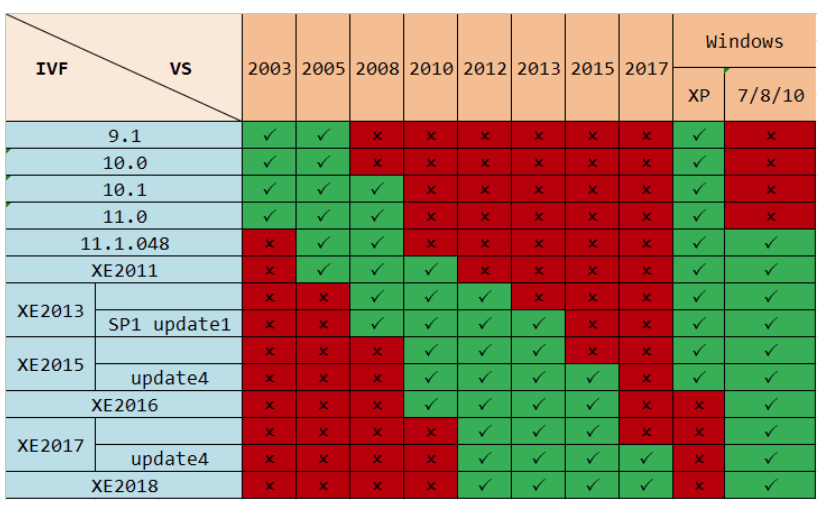
Company: https://www.sirris.be/aerosol-jet-printing
OPTOMEC: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m1YqgEGrbPQ
A review of aerosol jet printing—a non-traditional hybrid process for micro-manufacturing
Abstract
Aerosol Jet Printing (AJP) is an emerging contactless direct write approach aimed at the production of fine features on a wide range of substrates. Originally developed for the manufacture of electronic circuitry, the technology has been explored for a range of applications, including, active and passive electronic components, actuators, sensors, as well as a variety of selective chemical and biological responses. Freeform deposition, coupled with a relatively large stand-off distance, is enabling researchers to produce devices with increased geometric complexity compared to conventional manufacturing or more commonly used direct write approaches. Wide material compatibility, high resolution and independence of orientation have provided novelty in a number of applications when AJP is conducted as a digitally driven approach for integrated manufacture. This overview of the technology will summarise the underlying principles of AJP, review applications of the technology and discuss the hurdles to more widespread industry adoption. Finally, this paper will hypothesise where gains may be realised through this assistive manufacturing process.
aerosol jet vs ink jet
Dear Mr. Jiang,in my opinion, there are three major differences between the aerosol jet and ink-jet printing:1. Print resolution;2. Viscosity of ink (suspensions);3. The distance from the printhead to the substrate.1. Aerosol printing allows to achieve a higher print resolution, namely, almost 2-4 times higher than inkjet.(Typical resolution printing with a of aerosol jet is 10 microns, several studies reported print resolution of about 5 microns, while using typical ink jet printing is a minimum resolution of 20-25 microns).2. Method of aerosol jet have less strict requirements for the viscosity of ink (suspension), and therefore, a larger amount of materials (including ceramics, metals, etc.) can be printed by using an aerosol jet.(Typical range of viscosity of ink (suspension) for aerosol jet is in the range from 0.5 to 2000 cP, while the ink jet ink is used with a low viscosity, typically less than 20 cP).3. Aerosol jet has a greater opportunity to vary the distance between the print head to the substrate. Therefore, it is possible to print on non-flat (non-smooth) substrates. In of aerosol jet is possible to create 3D-contacts that inkjet is practically impossible.(A typical distance between the print head to the substrate in the aerosol jet is 1-5 mm, while the ink jet distance is fixed and must be equal, typically 1 mm)However, it is worth noting that the technology of aerosol printing is a younger technology compared to inkjet printing, the 2000s and 1950s, respectively. Consequently, the ink-jet printing more advanced technology, and you have more opportunities to find how to use inkjet printing to apply those or other structures. I also think that inkjet printing is a cheaper way of printing.
For comparison, an industrial aerosol jet printer costs about 500k USD, and the industrial inkjet printer about 200k USD, although it can be found for 50k USD (as a reference).Regarding the possibilities to form structures using ceramic materials and aerosol jet, I recommend the following article: DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.09.094.The last article compared the aerosol jet and ink-jet printing can be found here: DOI: 10.1021/ie503636cSee also the attached picture (Aerosol jet vs Ink Jet.gif).

- Aerosol jet vs Ink Jet.jpg320.86 KB
Cite19 Recommendati